Rhythmic gymnastics melds grace, athleticism, and art into a captivating display of skill and precision. Originating in the early 20th century, this discipline has integrated elements of ballet, dance, and gymnastics, capturing the fascination of audiences worldwide. With the popularity of rhythmic gymnastics on the rise, especially during Olympic seasons, let’s jump into the latest news, developments, and stars that are shaping this remarkable sport.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Rhythmic Gymnastics
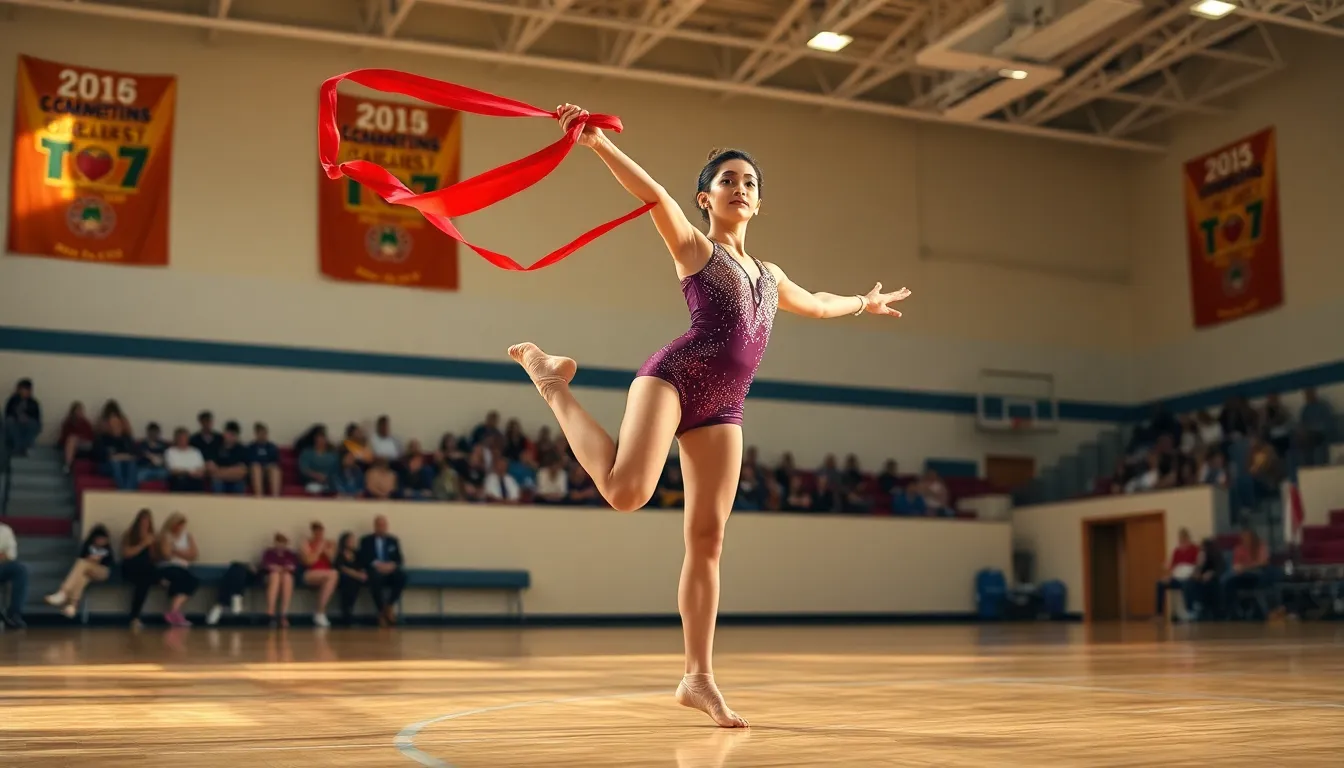

Rhythmic gymnastics is a unique Olympic sport that combines elements of gymnastics, dance, and choreography with five distinct apparatuses: the ball, hoop, ribbon, clubs, and rope. These events not only showcase individual talent but also emphasize artistry and creativity, making it a visually stunning spectacle for viewers. Competitors perform routines set to music, characterized by flowing movements, intricate footwork, and impressive body control. This sport requires extensive training, dedication, and an understanding of artistic expression, as athletes are judged on their technical skills, execution, and artistic impression.
Recent Developments in the Sport
In recent years, rhythmic gymnastics has seen a wave of innovations and changing trends. One of the most notable developments has been the introduction of new scoring systems. The International Gymnastics Federation (FIG) implemented a more transparent judging process that allows for greater accountability and clarity in scoring, addressing previous criticisms about bias. Also, there has been a push for diversity in routines, with athletes increasingly incorporating styles from various dance genres, further broadening the appeal of the sport. The growth of social media platforms has allowed gymnasts to showcase their talent globally, drawing in younger audiences and new fans.
Key Competitions and Events
Rhythmic gymnastics is highlighted by several major competitions throughout the year, including the World Championships and continental events such as the European Championships. These competitions not only serve as stepping stones for athletes aiming for Olympic gold but also as stages for showcasing emerging talents. The Tokyo 2020 Olympics, held in 2021, highlighted the sport on an international scale, with many countries having strong representation. Looking ahead, the Paris 2024 Olympics promises to bring further excitement, with athletes vying for glory on one of the world’s most prestigious platforms.
Emerging Talents and Stars
With rhythmic gymnastics evolving, several young talents have risen to prominence, captivating audiences with their extraordinary abilities and charisma. Athletes like Dina Averina from Russia and Linoy Ashram from Israel have made headlines for their extraordinary performances and contributions to the sport. Averina, a multiple-time world champion, is known for her exceptional ball routines that blend technical precision with emotive expression. Meanwhile, Ashram made waves by winning gold in the individual all-around at the Tokyo Olympics, becoming a household name. These competitors inspire upcoming gymnasts and help elevate rhythmic gymnastics’ status globally.
Techniques and Training Regimens
Training in rhythmic gymnastics requires a combination of physical conditioning, technical skill development, and artistic training. Athletes typically engage in diverse workouts, including strength training, flexibility exercises, and dance classes. Specific techniques such as coordination and balance are crucial, as athletes must master the use of their apparatus while performing complex body movements. Coaches often emphasize the importance of mental focus, as routines require not only physical prowess but also the ability to convey emotion and tell a story through movement. The balance between discipline and creativity is what eventually elevates a gymnast’s performance.
The Role of Technology in Rhythmic Gymnastics
Technology has increasingly influenced rhythmic gymnastics, from training to performance analysis. Advanced video analysis software helps coaches break down routines, providing insights that allow athletes to refine their skills. Also, wearable technology, like heart rate monitors and motion trackers, aids in tracking physical performance data, helping athletes optimize their training regimens. On the artistic side, enhancements in costume design have also emerged, with more advanced materials allowing for visually stunning outfits that complement performances. As technology continues to evolve, its integration into rhythmic gymnastics will likely foster further advancements in athlete performance and audience engagement.
Conclusion
Rhythmic gymnastics stands at a thrilling crossroads, where tradition meets modernity and athleticism intertwines with artistry. Recent developments, emerging talents, and the growing role of technology are shaping the landscape of this sport, making it more accessible and appealing to a global audience. As the world eagerly anticipates the next Olympic games, rhythmic gymnastics will undoubtedly sparkle on the international stage, inspiring the next generation of gymnasts and captivating fans with its beauty and complexity.